In the age of intelligent automation, AI agents are no longer just tools for data analysis or content generation—they are becoming orchestrators of action, capable of responding to events, making decisions, and triggering results across dozens of apps and systems.
At the core of this orchestration revolution lies Zapier, the industry-standard platform for workflow automation. But when paired with AI agents, Zapier becomes far more than a simple “if-this-then-that” utility—it becomes the operational backbone for autonomous, multi-platform AI-driven systems.
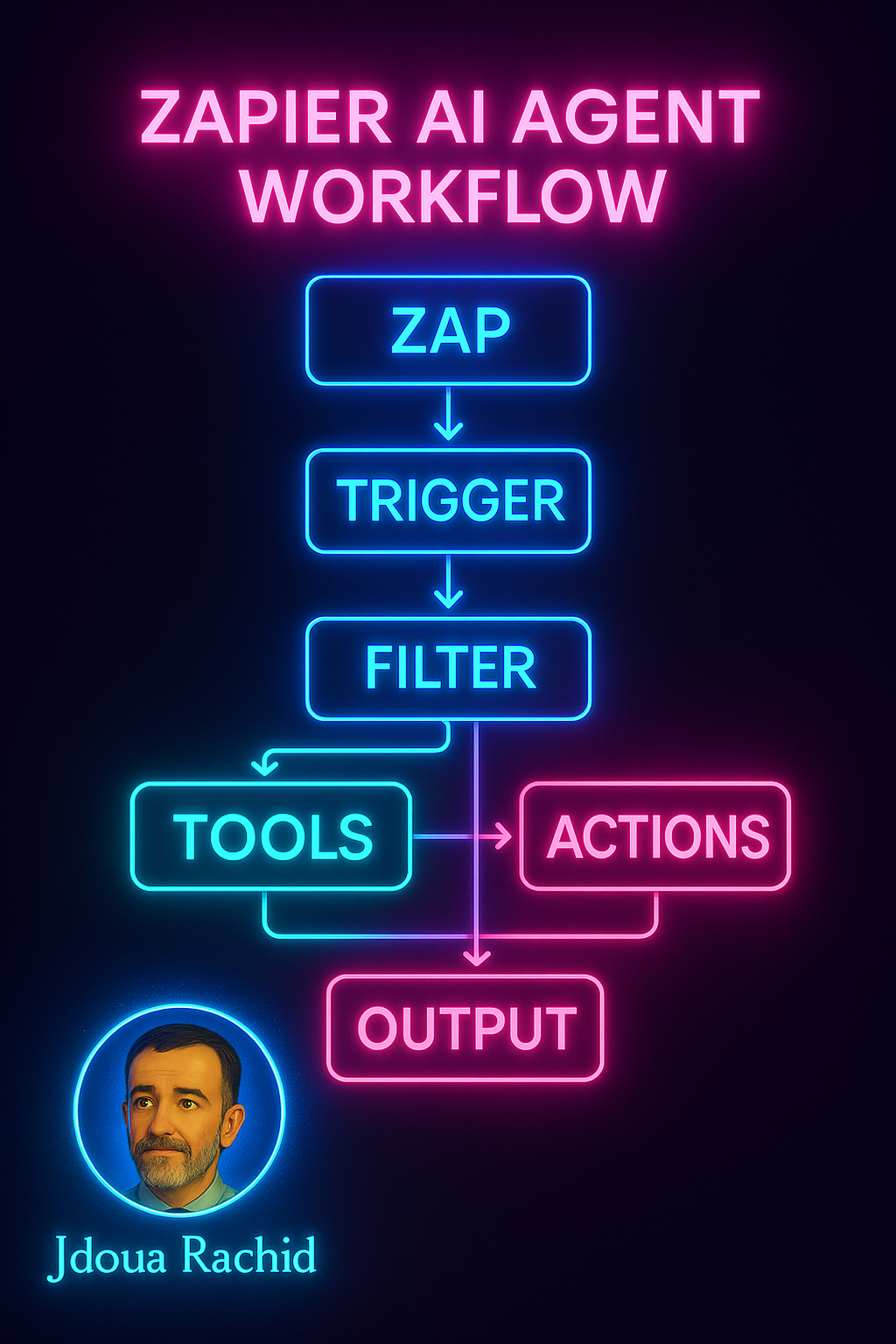
The infographic above outlines the essential Zapier AI Agent Workflow—a clear, actionable roadmap for building intelligent automations with precision. This workflow consists of six major stages:
- Zap
- Trigger
- Filter
- Tools
- Actions
- Output
Let’s break down each layer and see how, together, they allow AI agents to perform real-time, intelligent task execution at scale.
1. ZAP: Defining the Automation Logic.
A Zap is the foundational unit in Zapier. It is a self-contained automation made up of an event-trigger and one or more actions.
In an AI-powered context, a Zap is the container that enables the agent to operate autonomously—listening to signals, retrieving inputs, and acting accordingly.
Example AI Zaps:
- Auto-summarize emails from new clients using GPT and log them in Notion
- Trigger a sentiment analysis model on every new tweet mentioning your brand
- Process leads from a CRM with AI and notify sales if the lead score is high
Zaps empower agents to go from passive models to event-driven autonomous systems.
2. TRIGGER: Activating the AI Agent.
The Trigger is the event that tells Zapier (and your AI agent) that it’s time to act.
Triggers can be:
- A new row in a Google Sheet
- A form submission from Typeform
- An incoming webhook from another system
- A Slack message with a specific keyword
- A new customer added in HubSpot
For AI agents, the trigger acts as the signal that launches cognition. It sets off the chain of actions that turn passive data into active decision-making.
Best Practice: Ensure triggers are precise and meaningful. For example, instead of triggering on “any email received,” trigger on “emails with ‘proposal’ in the subject line.”
3. FILTER: Conditional Logic Before Execution.
Filters act as the first layer of reasoning. Before handing a task over to an AI or triggering a tool, the Filter stage asks:
“Does this input meet the criteria for action?”
This step is essential to avoid wasting tokens, compute power, or cloud calls.
Use Cases for Filters:
- Only respond to leads with company size > 100 employees
- Analyze sentiment only if the message contains negative language
- Only send customer data to the AI model if the form is fully complete
Think of this step as your AI agent’s internal gatekeeper—ensuring it works only on tasks worth its attention.
4. TOOLS: Connecting the AI Brain to External Utilities .
Tools refer to the external services and utilities that support the AI agent’s reasoning or enrich its capabilities. These can be databases, APIs, retrieval functions, or plugin-based modules.
In Zapier, tools can be:
- Google Sheets (for memory)
- Webhooks (for sending/receiving data to/from any app)
- OpenAI or Claude (for generating text)
- Notion, Airtable, or Firebase (for structured outputs)
- LangChain or DSPy integrations (for advanced reasoning)
Zapier allows you to plug these tools into your agent’s workflow, enabling it to think, fetch, store, or validate information before acting.
Practical Example:
A Zap may pull in the last three support tickets from Zendesk before letting GPT generate a personalized email reply—thus ensuring memory and context.
5. ACTIONS: What the Agent Does .
After collecting the input and verifying it through filtering and external tools, your AI agent reaches the Action stage—this is where it executes decisions or produces results.
Examples of AI-powered actions:
- Write a summary using OpenAI
- Send a Slack message with the result
- Create a Trello card based on agent-generated project tasks
- Auto-respond to customer requests using a templated GPT reply
- Upload a document to Google Drive after processing
The Action block can also include multi-step execution, such as:
- Summarize → Translate → Send
- Extract Data → Validate → Visualize
This is the operational arm of the Zapier AI agent—where the intelligence turns into tangible action.
6. OUTPUT: Delivering the Results .
Finally, every agent must produce an output—a tangible result, message, or handoff to another system or user.
Output can be:
- A JSON payload sent to another platform
- An email to the user
- A push notification or Slack message
- A filled-in field in a database
- A visual report posted to a dashboard
In agent-based workflows, the Output block often feeds into another Zap or agent—continuing the chain of automation. This turns your AI agent from a standalone assistant into a node in a larger ecosystem.
Best Practices for Outputs:
- Include status updates or confirmations (e.g., “report generated”)
- Format outputs clearly and consistently
- Use Zapier Paths or Webhooks to pass results to next agents
Real-World Applications of the Zapier AI Agent Workflow :
The flexibility of this workflow makes it incredibly powerful across industries:
✅ Marketing Automation
- Trigger on new email subscribers → Analyze preferences → Draft welcome emails → Auto-schedule newsletters
✅ Customer Support
- New Zendesk ticket → Classify urgency → Auto-draft reply → Alert support tier if critical
✅ Sales Intelligence
- New CRM lead → Enrich via Clearbit → Score with GPT → Send high-value leads to Slack
✅ Project Management
- Trello card creation → Analyze complexity → Assign estimated effort → Notify PM with recommendations
✅ Legal Ops
- Upload of contract → Auto-summarize clauses → Flag missing terms → Notify legal reviewer
In each case, the AI agent uses this exact Zapier workflow to decide, act, and deliver with minimal human input.
Building a Zapier AI Agent in Practice :
Here’s how you can build your own Zapier AI-powered agent:
- Create a new Zap
- Set your Trigger (e.g., webhook, email, or form submission)
- Add a Filter to qualify the input
- Connect to external Tools (e.g., OpenAI, Google Sheets)
- Define one or more Actions using Zapier’s app library
- Format and send the final Output
- Monitor results and iterate based on performance logs
The Future of AI + Zapier :
As AI agents become more powerful with memory, tool use, planning, and adaptive logic, Zapier is positioned to become the enterprise-grade orchestration layer for intelligent automation.
Future upgrades will likely include:
- Multi-agent orchestration across Zaps
- AI planning modules (e.g., planners and feedback loops)
- Agent memory via persistent Zapier storage or vector databases
- Voice and multimodal triggers
Final Thoughts: Zapier as the Brainstem of AI Agents :
While AI agents offer cognition, insight, and creativity—Zapier offers structure, logic, and execution.
The Zapier AI Agent Workflow combines:
- Precision (Trigger + Filter)
- Intelligence (Tools + AI)
- Action (Execution + Output)
…into one seamless system.
Whether you’re a solopreneur, enterprise architect, or AI engineer, this workflow is your playbook for designing scalable, intelligent automations that operate 24/7 across your digital ecosystem.
Unlock the full power of AI automation today. For expert tutorials, blueprints, and case studies, subscribe to: 👉 https://airevolutiondigest.com
#ZapierAI #AIWorkflow #AgentAutomation #LLMAgents #ZapierZaps #OpenAIIntegration #NoCodeAI #AIProductivity #AgentOrchestration #AITriggerAutomation